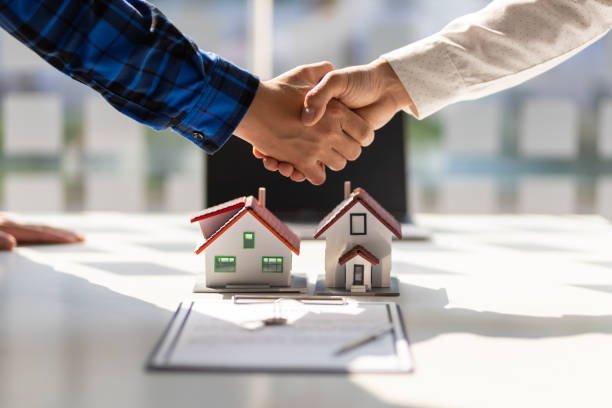
Purchasing a home involves several legal considerations and processes to safeguard your interests and ensure a smooth transaction. Here’s a comprehensive overview of the key legal aspects involved in buying a home, including the Massachusetts offer to purchase real estate form and the closing procedures:
The Purchase Agreement
Offer and Acceptance:
The process starts with the buyer submitting an offer through a legally binding document known as a purchase agreement.
The offer only becomes binding upon the seller’s acceptance, establishing a contractual relationship.
Contingencies:
Financing Contingency: Allows the buyer to cancel the contract if suitable mortgage financing cannot be secured.
Inspection Contingency: Permits the buyer to inspect the property and negotiate repairs or cancel the contract if significant issues are found.
Appraisal Contingency: Protects the buyer if the property doesn’t appraise for the agreed purchase price.
Title Contingency: Ensures the seller has a clear title to the property, free from encumbrances or legal disputes.
Home Inspection:
A comprehensive home inspection evaluates the property’s condition, including structural, mechanical, and safety aspects.
The inspection report informs the buyer’s decisions on moving forward, negotiating repairs, or withdrawing from the transaction.
Title Search:
A thorough title search verifies that the property’s title is free of hidden liens, encumbrances, or legal issues.
Typically conducted by a real estate attorney or a title company.
III. Closing Procedures
Escrow and Earnest Money:
The buyer deposits earnest money into an escrow account to demonstrate commitment.
Earnest money is usually refunded if the contract is canceled due to specified reasons.
Closing Disclosure:
The Closing Disclosure provides a detailed breakdown of the financial aspects of the transaction.
It outlines the final purchase price, closing costs, loan terms, and other vital financial information.
The Closing:
The closing, also known as settlement or escrow, is the final stage in the homebuying process.
Both the buyer and seller, along with their agents and attorneys, sign necessary legal documents, including the deed and mortgage documents.
Ownership is formally transferred during the closing, and the transaction is recorded with the local government office.
Title Transfer:
During the closing process, the seller formally transfers ownership to the buyer.
This transfer is recorded with the local government office, legally establishing the buyer’s ownership rights.
The buyer receives the keys to their new property, marking the completion of the purchase.
Conclusion:
Understanding the legal aspects of purchasing a home is crucial for protecting your investment and ensuring a successful transaction. Seek guidance from experienced professionals, such as real estate agents, attorneys, and inspectors, to navigate the complexities of homebuying. Each real estate transaction is unique, so thorough research and legal considerations are essential for a secure and compliant process. By being well-informed and prepared, you can achieve your dream of homeownership while maintaining a legally sound transaction.