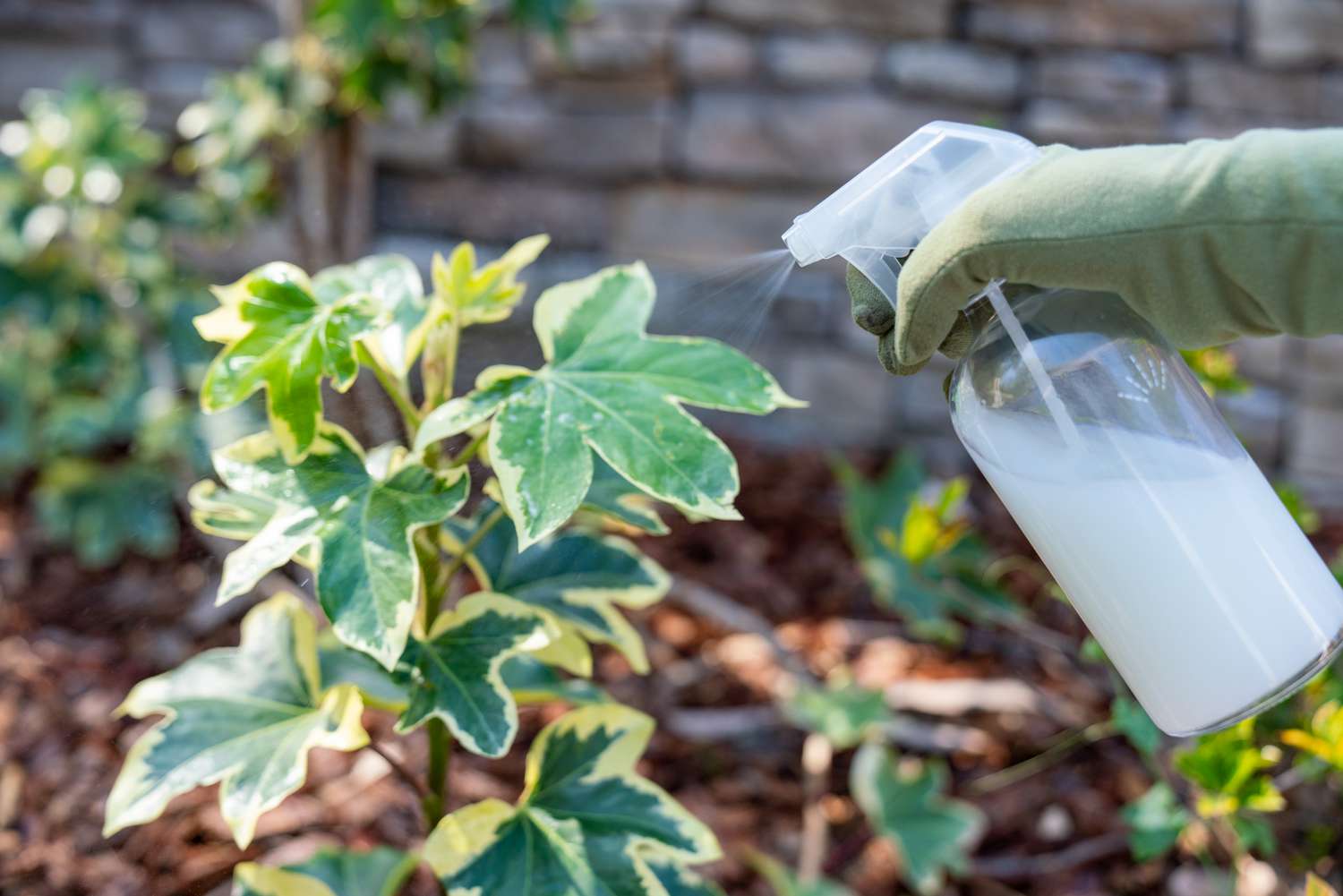
Subheading: The Milk Fertilizing Trend
Social media platforms like TikTok often feature various unconventional gardening hacks, including the idea of fertilizing houseplants with milk. This trend has gained traction, with some users advocating for using milk as a natural fertilizer to promote plant growth and health. However, despite its popularity online, there are reasons to approach this practice with caution.
Subheading: Understanding the Theory Behind Milk Fertilization
Proponents of using milk as a fertilizer claim that its calcium content can benefit plants, particularly those that require calcium for growth and development. They argue that milk provides essential nutrients and proteins that can nourish the soil and enhance plant vitality. Additionally, some suggest that milk’s antibacterial properties may help suppress fungal growth in the soil.
Subheading: Potential Risks and Drawbacks
While the idea of using milk as a fertilizer may seem appealing, there are several potential risks and drawbacks to consider. First and foremost, milk is organic matter that can decompose when exposed to heat and moisture, leading to unpleasant odors and attracting pests such as insects and rodents. Additionally, milk may introduce harmful bacteria and pathogens into the soil, posing a risk to plant health.
Subheading: Impact on Soil pH and Microbial Balance
Another concern with using milk as a fertilizer is its effect on soil pH and microbial balance. Milk is slightly acidic, and repeated applications can alter the pH of the soil, making it less hospitable to beneficial microorganisms essential for nutrient cycling and plant health. Moreover, excessive milk residues can create an anaerobic environment in the soil, hindering root growth and nutrient uptake.
Subheading: Environmental Considerations
From an environmental perspective, the use of milk as a fertilizer raises questions about sustainability and resource management. Milk is a valuable food product that requires significant resources, including water and energy, for production and processing. Pouring milk into the soil for gardening purposes may be seen as wasteful, especially considering alternative, more eco-friendly fertilization methods.
Subheading: Science-Based Alternatives
Instead of relying on unproven gardening hacks promoted on social media, it’s advisable to use science-based fertilization methods backed by research and expertise. Commercial fertilizers formulated specifically for plant growth contain balanced nutrients tailored to meet the needs of different plant species. Additionally, organic alternatives such as compost and compost tea provide natural sources of nutrients and support soil health without the risks associated with milk fertilization.
Subheading: Sustainable Gardening Practices
In pursuit of sustainable gardening practices, it’s essential to prioritize soil health and ecosystem balance. Incorporating organic matter into the soil, practicing crop rotation, and implementing water-saving techniques can promote long-term sustainability and resilience in the garden. By adopting holistic approaches to gardening, individuals can cultivate thriving, environmentally-friendly landscapes without resorting to potentially harmful shortcuts.
Subheading: Educating and Informing Others
As misinformation spreads rapidly on social media platforms, it’s crucial to educate and inform others about evidence-based gardening practices. Encouraging critical thinking and skepticism towards viral gardening trends can help prevent the spread of misinformation and promote responsible gardening practices. By sharing reliable information and resources, gardeners can empower themselves and others to make informed decisions about plant care and cultivation.
Subheading: Conclusion: Proceeding with Caution
While social media may offer enticing shortcuts and hacks for gardening, it’s essential to approach them with caution and skepticism. The trend of fertilizing houseplants with milk, while popular online, carries potential risks and drawbacks that could harm plant health and soil quality. By prioritizing science-based methods and sustainable practices, gardeners can nurture healthy, thriving plants while minimizing environmental impact.